Home-based transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) in Alzheimer's disease: rationale and study design, Alzheimer's Research & Therapy
By A Mystery Man Writer
Description
Background Gamma (γ) brain oscillations are dysregulated in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and can be modulated using transcranial alternating stimulation (tACS). In the present paper, we describe the rationale and design of a study assessing safety, feasibility, clinical and biological efficacy, and predictors of outcome of a home-based intervention consisting of γ-tACS over the precuneus. Methods In a first phase, 60 AD patients will be randomized into two arms: ARM1, 8-week precuneus γ-tACS (frequency: 40 Hz, intensity: 2 mA, duration: 5 60-min sessions/week); and ARM2, 8-week sham tACS (same parameters as the real γ-tACS, with the current being discontinued 5 s after the beginning of the stimulation). In a second phase, all participants will receive 8-week γ-tACS (same parameters as the real γ-tACS in the first phase). The study outcomes will be collected at several timepoints throughout the study duration and include information on safety and feasibility, neuropsychological assessment, blood sampling, electroencephalography, transcranial magnetic stimulation neurotransmitter measures, and magnetic resonance imaging or amyloid positron emission tomography. Results We expect that this intervention is safe and feasible and results in the improvement of cognition, entrainment of gamma oscillations, increased functional connectivity, reduction of pathological burden, and increased cholinergic transmission. Conclusions If our expected results are achieved, home-based interventions using γ-tACS, either alone or in combination with other therapies, may become a reality for treating AD. Trial registration PNRR-POC-2022–12376021.
1x1 tACS Device - Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation – Soterix Medical

Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS): from basic mechanisms towards first applications in psychiatry
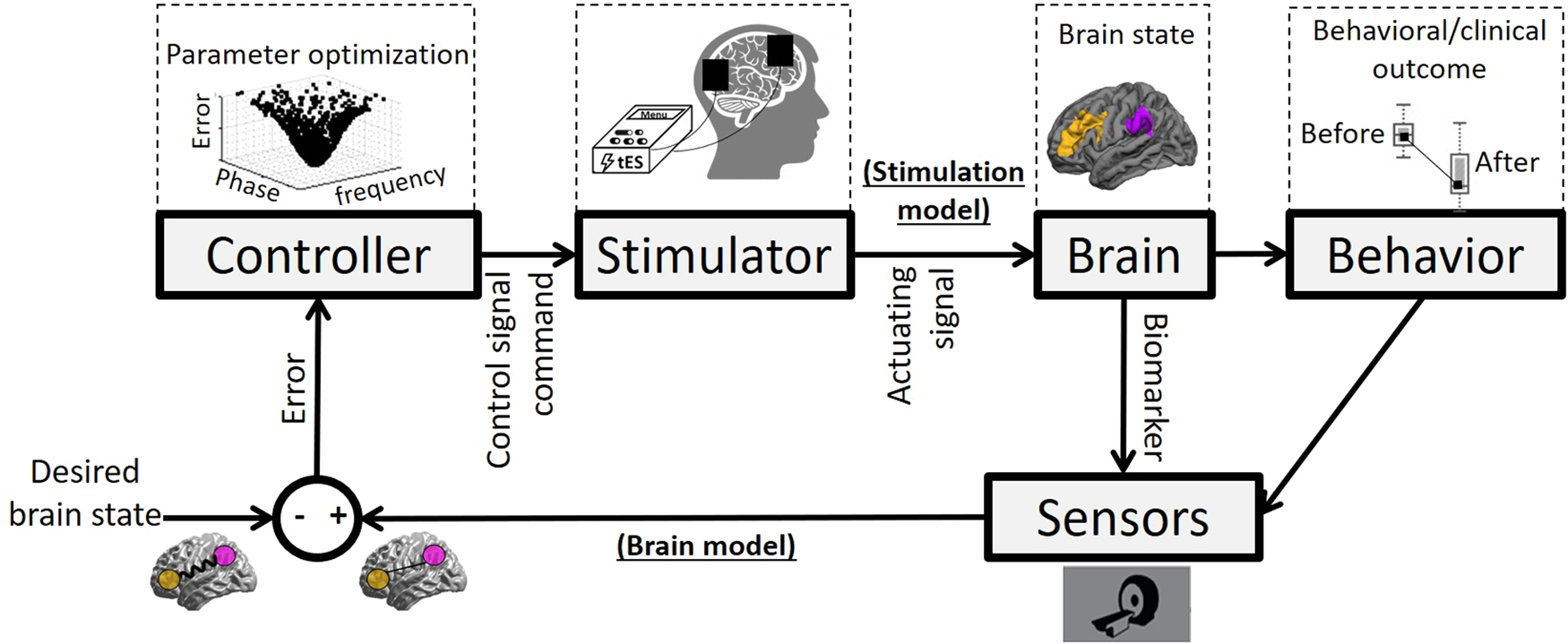
Closing the loop between brain and electrical stimulation: towards precision neuromodulation treatments

Medication use after transcranial alternating current stimulation
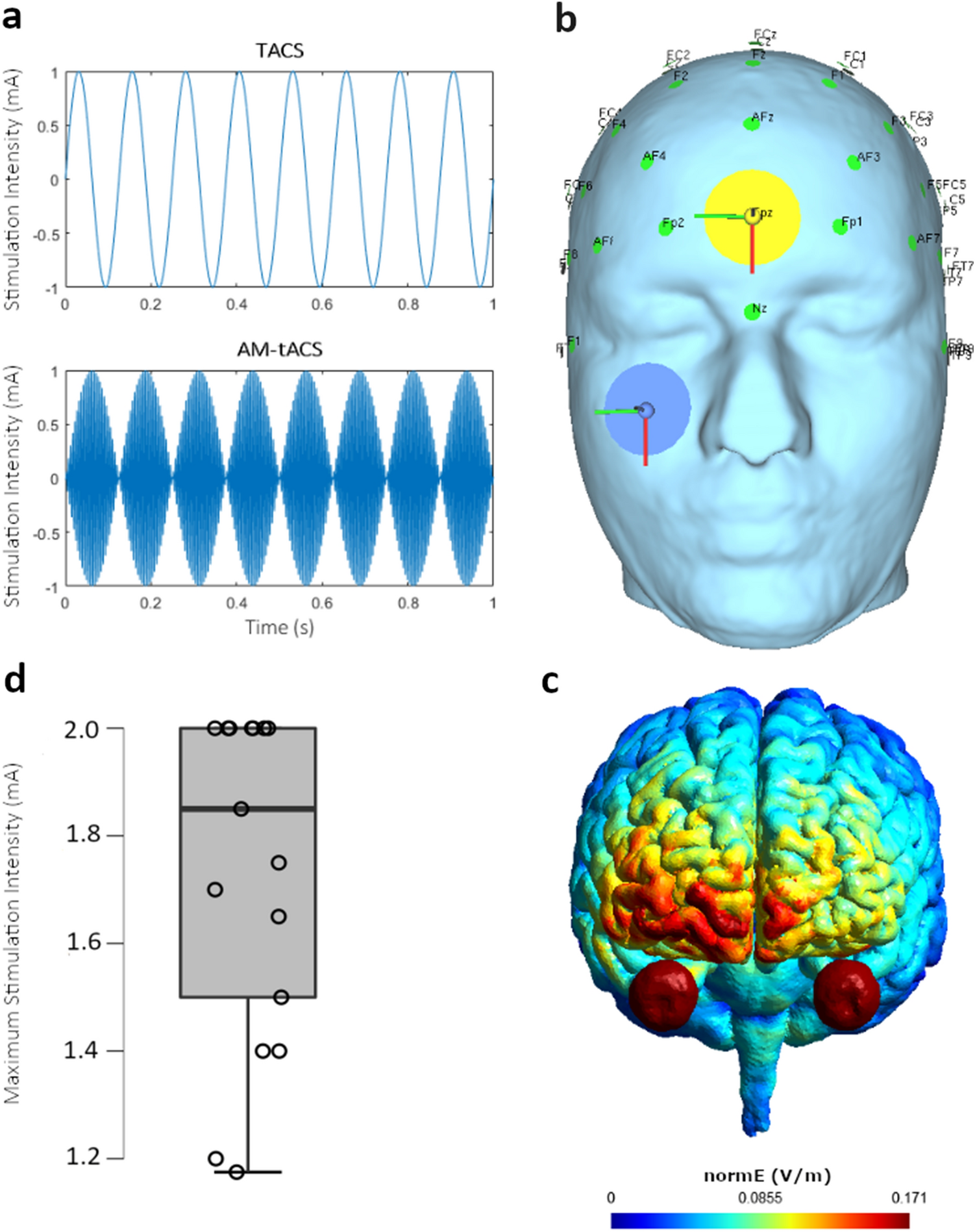
Amplitude modulated transcranial alternating current stimulation (AM-TACS) efficacy evaluation via phosphene induction

PDF) Exposure to gamma tACS in Alzheimer's disease: A randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled, crossover, pilot study
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS): from basic mechanisms towards first applications in psychiatry
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Transcranial magnetic stimulation distinguishes Alzheimer disease
from
per adult (price varies by group size)